How is VPN call established using CAMEL support.
The VPN service translates the dialled number into the public number associated with the destination subscriber, who belongs to the same VPN group as the calling subscriber. Hence,
subscribers of one VPN group, e.g. an enterprise, may call one another by GSM, by dialling the
PABX extension number.
subscribers of one VPN group, e.g. an enterprise, may call one another by GSM, by dialling the
PABX extension number.
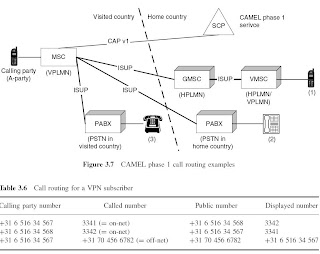
In case (1), the CAMEL service connects the calling subscriber to a mobile VPN subscriber. The mobile VPN subscriber belongs to the same VPN group as the calling subscriber. The call is routed to the GMSC of the HPLMN operator, from where the call is routed to the VMSC, where the called subscriber currently resides.
In case (2), the calling subscriber is connected to an extension of the PABX at the company.
In example (3), the calling subscriber is connected to a VPN colleague in an office in the visited country.
In all three cases, the ISUP signalling may take the shortest possible path between the VMSC of the calling subscriber and the PSTN/PLMN of the called subscriber. In these examples, the VPN service may ensure that the called party receives the calling party’s VPN number on her display, instead of the calling party’s public number (Table 3.6).
On-net calls are calls between users of the same VPN group;
Off-net calls are calls from a user of a VPN group to a user outside the VPN group or vice versa.
Referring to the diagram below:
When the calling party (+31 6 516 34 567) dials 3341, the VPN service determines that this number belongs to a subscriber of the same VPN group. The VPN service translates the dialled
number into the public GSM number of the destination subscriber (+31 6 516 34 568). The VPN
service also provides an additional calling party number (3342) in CAP CON. The called subscriber receives 3342 on her display, instead of +31 6 516 34 567. Should the called VPN subscriber return the call, i.e. dial 3342, then the VPN service will connect the call to +31 6 516 34 567. If the calling subscriber dials an off-net number (e.g. +31 70 456 6782), then the VPN service allows the call to continue to the dialled destination, without affecting the routing of the call. VPN does not provide an additional calling party number, since the VPN number should not be presented to a called party that does not belong to the (same) VPN group.
When a call crosses an international boundary, it may occur that the calling party number or the
additional calling party number is not transported in the ISUP signalling link.
A VPN subscriber may receive an on-net call when she is roaming in a non-CAMEL network. In
that case, the VPN service for that called subscriber may remove the additional calling party number from the ISUP signalling flow. The rationale is that the called VPN subscriber might otherwise return a call to the displayed VPN number of the calling party. However, since the network where the called party is currently roaming does not support CAMEL, the VPN service does not have the capability to connect a call from that subscriber to a VPN destination.
